Exercise 1.9.9. Write as the ratio of two integers: −19. 8.41. Answer. Let's look at the decimal form of the numbers we know are rational. We have seen that every integer is a rational number, since a = a 1 for any integer, \ ( a\). We can also change any integer to a decimal by adding a decimal point and a zero.. Of course, if we name something the real numbers, there must be numbers that aren't real. Otherwise, they'd just be called the numbers. One such not real number, one that cannot be a length, is − 1 − 1. It is part of a collection of numbers called the complex numbers, it is denoted with the letter i i. As an extension, the square root of.

Real number (Part1) YouTube
.PNG)
A Review of Basic Algebra Presentation Mathematics

বাস্তব সংখ্যা (Real Number) JUMP Magazine

Beautiful Math
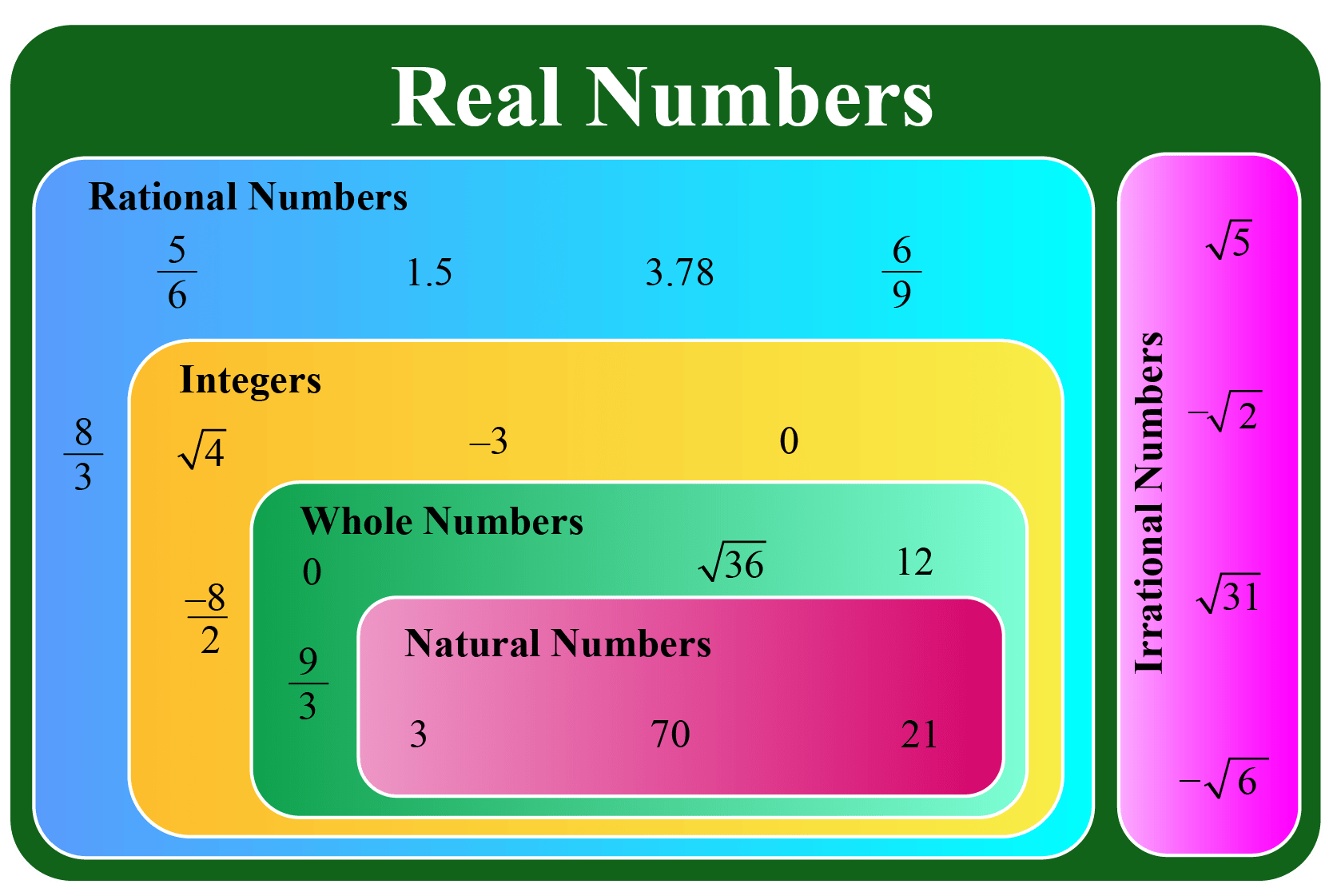
Which Property Of Real Numbers Is Shown Below

Number 1 / นัมเบอร์วัน

Real number (वास्तविक संख्या) इससे बाहर एग्जाम में कुछ भी नहीं रहेगा by dhairya sir संघर्ष
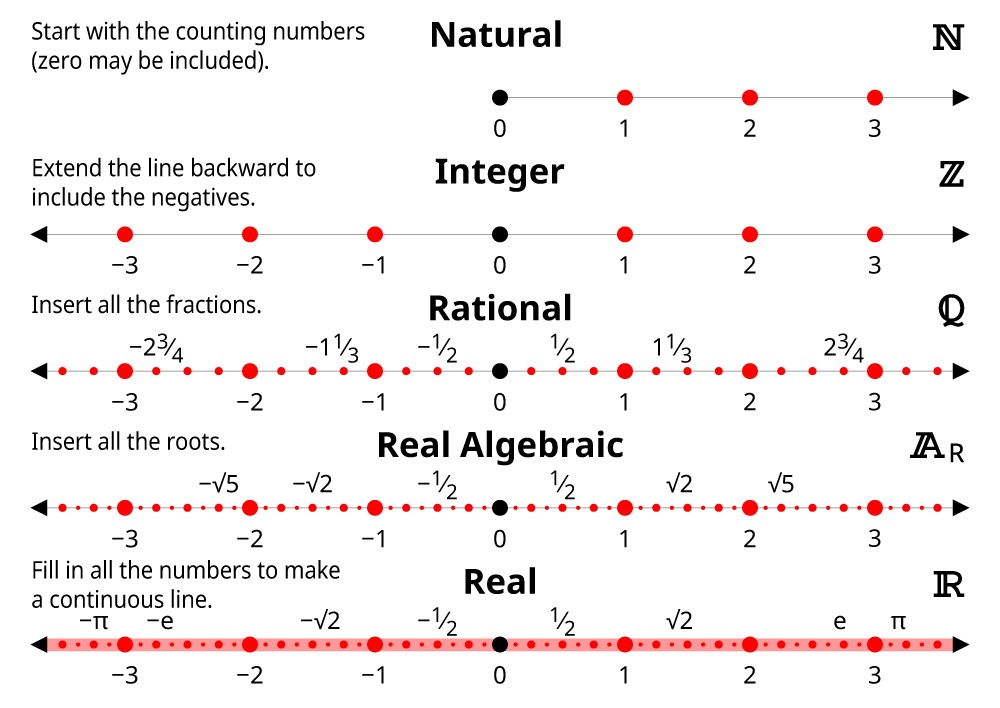
Number Sets

1.1 THE REAL NUMBER SYSTEM
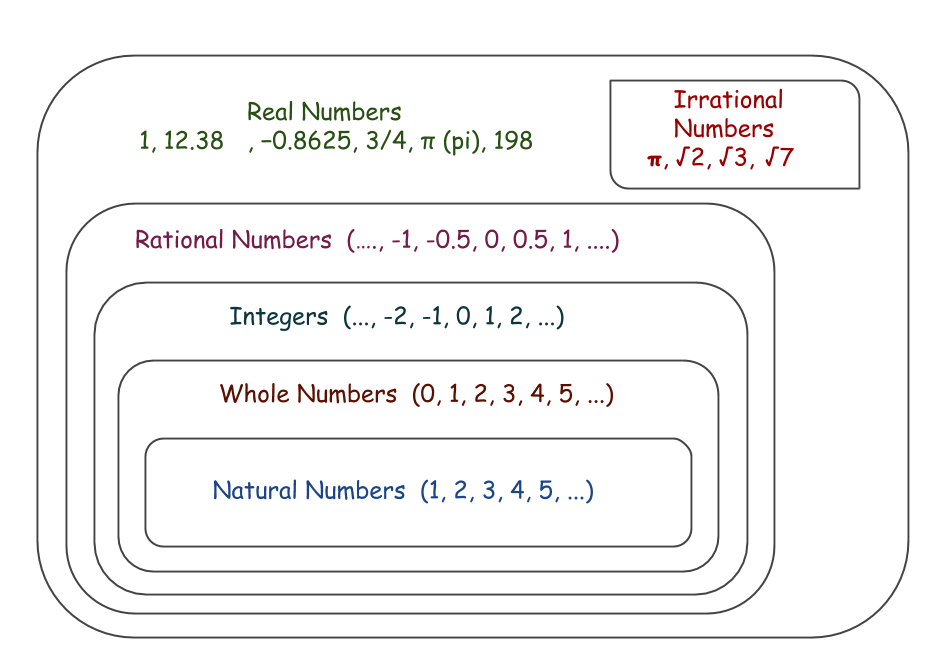
Real Numbers Maths eLab

Real Numbers K.Nisa)

Lesson 1 Real Numbers and Integer Exponent UNIT I REAL NUMBER AND REAL LINE 1 CONCEPT OF SET

จำนวนจริง ( Real Number ) คณิตศาสตร์ Tuemaster เรียนออนไลน์ ม.ปลาย

Real Number _वास्तविक संख्या बनाना बच्चों का खेल है । Ncert Math । By Suraj Sir 1 YouTube

Real Number 1.2 part 3 YouTube

Maths Real Numbers part 1 (Real number System) CBSE class 10 Mathematics X YouTube

Real Number Exercise 1.4 Maths Class 10th Chapter 1 NCERT. YouTube

RD Sharma Solutions for Class 10 Maths Chapter 1 Real Numbers

จำนวนจริง(Real Number)คณิตศาสตร์ Tuemaster เรียนออนไลน์ ม.ปลาย
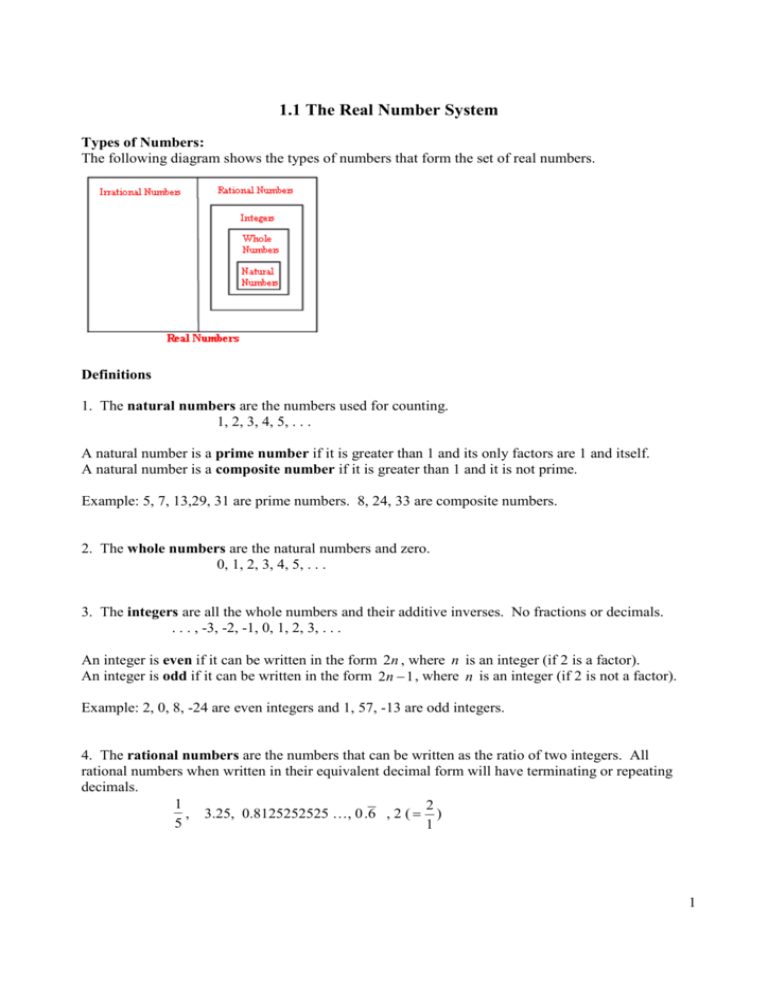
1.1 The Real Number System
In other words, a real number is any rational or irrational number, including positive and negative whole numbers, integers, decimals, fractions, and numbers such as pi ( π) and Euler's number ( e ). In contrast, an imaginary number or complex number is not a real number. These numbers contain the number i, where i2 = -1.. of addition For any real number a, a + (− a) = 0 − a is the additive inverse of a A number and its o p p o s i t e add to zero. of multiplication For any real number a, a ≠ 0 a · 1 a = 1 1 a is the multiplicative inverse of a A number and its r e c i p r o c a l multiply to one. of addition For any real number a, a + (− a) = 0 − a is.